We are developing medicine for disorders with chronic inflammation and for disorders, were the immune system is overwhelmed by inflammation and not able to heal the condition on its own.
Inflammatory Disease
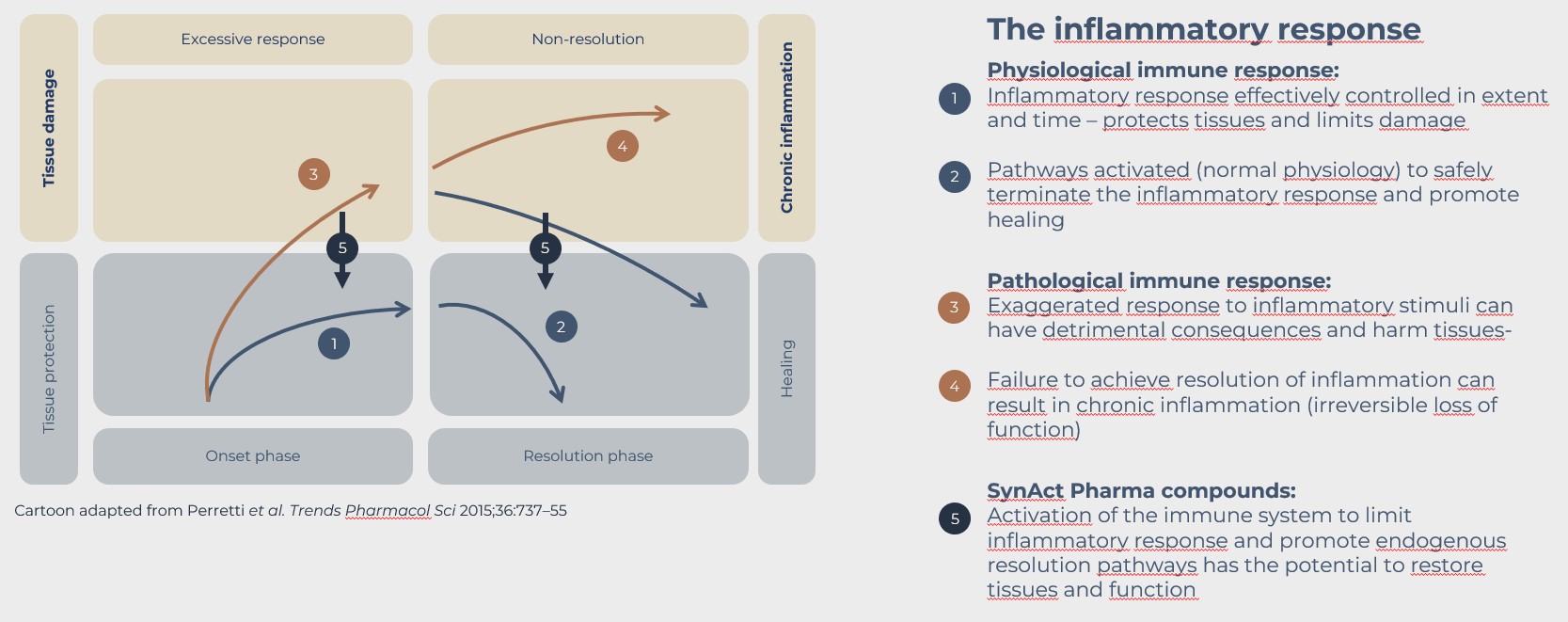
Inflammation is the immune system’s way of responding to infections or injuries. Normally an inflammatory response is self-limiting. The immune system will “deactivate” itself and the inflammation will be resolved after the invading pathogen has been removed or the injury has begun to heal.
However, in many cases inflammation can be excessive or chronic and it can overwhelm the immune system’s ability to resolve the inflammation. This can lead to pain, destruction of tissue, and loss of function (disability).

Autoimmune or chronic inflammatory diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are associated with an inappropriate inflammatory response that is not resolved through endogen mechanisms and therefore becomes chronic.
Other examples of diseases with uncontrolled inflammatory responses are virus infections such as respiratory virus including COVID-19 and a number of mosquito borne diseases such as Dengue fever associated with an exacerbated inflammatory response that brings the patient into a hyperinflammatory state with high risk for organ dysfunction where patients need hospitalization.
Currently, these inflammatory diseases are treated with various drugs including drugs that target the inflammatory response with the risk of suppressing the immune system to a degree that unwanted side effects develop.
Resolving Inflammation and Resetting the Immune System
Recent research has shown that resolution of inflammation is not a passive process, but it can be promoted by activating certain biological pathways, and thereby inflammatory response may be treated without immune suppression.
When the immune system is overwhelmed, therapies may help resolve inflammation by providing both anti-inflammatory activity and by triggering the immune system’s natural inflammatory resolution mechanisms and contribute to the rebalancing of the immune system..
Most current treatment inhibit the immune system either by blocking specific pathways or by more unspecific means which in can lead to unwanted side effects. In contrast to this, our approach is to enable resolution of inflammation, and promote that the immune system reestablishes homeostasis, the condition where the biological systems are in balance.
The Melanocortin System Mediates Resolution of Inflammation
The melanocortin system is an ancient modulatory system comprising a family of 5 melanocortin receptors and a set of naturally occurring melanocortin peptides that bind to and activate these receptors.
A receptor is a protein, a large chain of amino acids, that binds other molecules specifically. Activation means that a signaling pathway is activated, when the other molecule binds.
In the case of melanocortin receptors, these are transmembrane receptors embedded in the cell membrane with a part exposed to the outside of the cell, and another part reaching inside the cell. When the melanocortin peptides bind to the receptors on the outside, the receptors activate processes inside the cells that determine their function.

The receptors are different in size and amino sequence so the space where the peptide or other molecules can bind allows for selective activation of the different subtybes of the melanocortin receptors (MC1R-MC5R). The receptors are located on many cell types with different functions and are spread throughout most of the body.

- MC1R and MC3R are believed to be the key receptors involved in direct effects on the immune system and these receptors are located on immune cells and associated structural and supportive cells.
- MC2R is primary expressed in the adrenal glands where stimulation is directly associated with the release of cortisol, a steroid, and due to side effects of too much steroid release, activation is not preferred.
- MC4R is primary found in the central nervous system and plays a pivotal role in central regulation of metabolism including food intake.
- MC5R is found in exocrine glands, expressed by some subtypes of immune-active cells in the eye among others.
When activated, MC1R and MC3R provide direct dual actions
1. It inhibit excess immune activity by reducing, but not blocking pro-inflammatory pathways, as influx of specific cells into inflamed tissue and release of pro-inflammatory mediators, and
2. stimulate direct pro-resolving pathways as specific cells ability to clean-up the inflammation.
Together this dual effect facilitates that the immune system is rebalanced at new beneficial immunological homeostatic setpoint clinically shown as relief of symptoms with the potential to restore normal function.
From the above it seems evident that the resolution therapy should be applied when active inflammation in present and can and should be introduced as soon as possible to get the immunological response under control before it induces irreversible loss of function. Either as first line treatment or as treatment in condition with exacerbations as flairs in RA or hyperinflammatory responses to viral infections.

